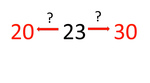Mathematics – United Kingdom – National Curriculum
Year 4 programme of study
KS2.Y4.N.NPV – Number - number and place value
Pupils should be taught to:
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.1 – Count in multiples of 6, 7, 9, 25 and 1,000
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
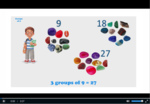
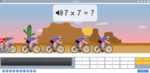
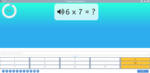
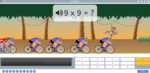
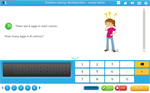
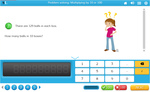
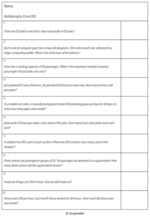
Samples: Groups of 6. Rows of 7. Groups of 9. Rows of 6. Groups of 7. Rows of 9.
-
Groups and rows of 6
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Groups and rows of 7
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Groups and rows of 9
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.2 – Find 1,000 more or less than a given number
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.3 – Count backwards through 0 to include negative numbers
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
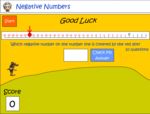
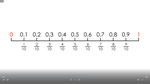
Samples: Negative numbers. Negative numbers on a number line. Negative numbers. Negative numbers.
-
Negative numbers on a number line
- Activities: 3 course, 1 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
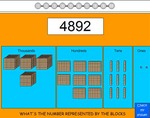
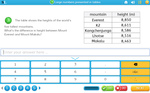
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.4 – Recognise the place value of each digit in a four-digit number (1,000s, 100s, 10s, and 1s)
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Expanded notation. Expanded notation. Expanded Notation. Expanded notation. Expanded notation.
-
Expanded notation
- Activities: 3 course, 4 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.5 – Order and compare numbers beyond 1,000
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Representing numbers (thousands). Great than or Less than. Representing numbers (thousands). Place Value to 1000.
-
Representing numbers (thousands)
- Activities: 3 course, 11 extra
-
Comparing numbers to 10,000 (<,=,>)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.6 – Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
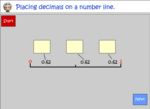
Samples: Expanded Notation Part 1. Placing Decimals On A Number Line. Compare and order decimals.
-
Place value of a digit
- Activities: 3 course, 1 extra
-
Decimals on a number line.
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
Compare and order decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
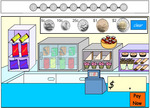
Paying for goods and services
- Activities: 1 course, 3 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.7 – Round any number to the nearest 10, 100 or 1,000
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Rounding to the nearest 10 (3 digits). Rounding to the nearest hundred. Rounding numbers: Activity 2.
-
Rounding to the nearest 10
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
Rounding to the nearest hundred
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.8 – Solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above and with increasingly large positive numbers
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
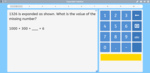
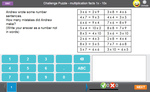
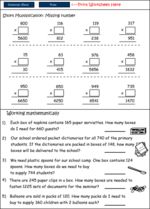
Samples: Challenge puzzle. Ordering large numbers No:1. Large numbers presented in tables. Paying for goods.
-
Challenge puzzle - Odd and Even Numbers
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Ordering large numbers
- Activities: 0 course, 6 extra
-
Large numbers presented in tables
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Paying for goods and calculating totals
- Activities: 1 course, 6 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.NPV.9 – Read Roman numerals to 100 (I to C) and know that over time, the numeral system changed to include the concept of 0 and place value
KS2.Y4.N.AS – Number - addition and subtraction
Pupils should be taught to:
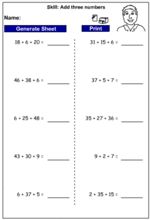
KS2.Y4.N.AS.1 – Add and subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using the formal written methods of columnar addition and subtraction where appropriate
-
13 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding on single digit numbers using blocks. Adding two digit numbers using blocks. Adding multiples of 10.
-
Adding on single digit numbers using blocks
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Adding two digit numbers using blocks
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
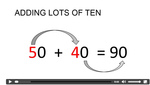
Adding multiples of 10
- Activities: 3 course, 4 extra
-
Adding three digit numbers using blocks
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Adding to make 100
- Activities: 5 course, 3 extra
-
Adding three numbers
- Activities: 6 course, 10 extra
-
Subtracting 10 using blocks
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
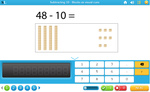
Subtracting multiples of 10 using blocks
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
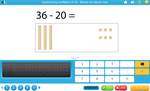
Place value - Subtract three digit numbers
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
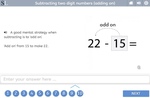
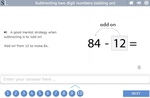
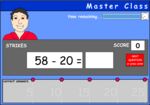
Subtracting two digit numbers (adding on)
- Activities: 5 course, 0 extra
-
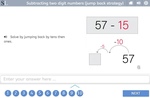
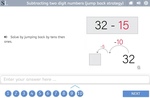
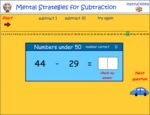
Subtracting two digit numbers (jump back strategy)
- Activities: 5 course, 16 extra
-
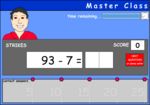
Subtracting two digit numbers (written strategy)
- Activities: 6 course, 10 extra
-
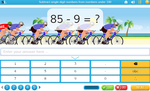
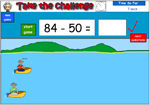
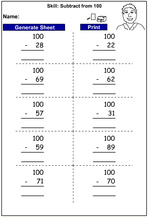
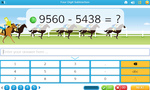
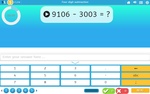
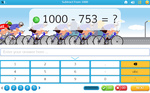
Subtracting large numbers
- Activities: 3 course, 14 extra
-
-
13 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.AS.2 – Estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding three digit numbers. Mental strategy for adding 3 numbers. Adding three numbers.
-
Three digit addition (Skill 48)
- Activities: 6 course, 7 extra
-
Mental strategies for adding three numbers (Skill 60)
- Activities: 5 course, 1 extra
-
Adding three numbers (Skill 61)
- Activities: 4 course, 7 extra
-
Four digit addition (Skill 62)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
Four digit subtraction (Skill 63)
- Activities: 6 course, 7 extra
-
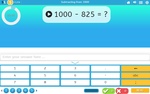
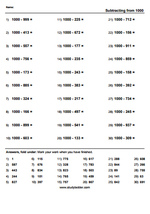
Subtracting from 1000 (Skill 64)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.AS.3 – Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding large numbers (problem solving). Addition of large numbers (puzzle). Subtraction - missing number.
-
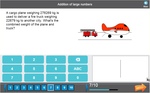
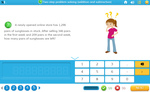
Adding large numbers (problem solving)
- Activities: 1 course, 8 extra
-
Addition of large numbers (puzzle)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Subtraction - missing number
- Activities: 1 course, 2 extra
-
Two step problem solving (addition and subtraction)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.MD – Number - multiplication and division
Pupils should be taught to:
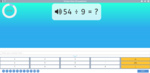
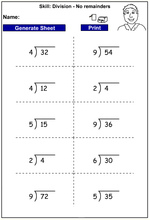
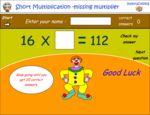
KS2.Y4.N.MD.1 – Recall multiplication and division facts for multiplication tables up to 12 × 12
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
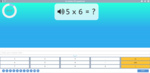
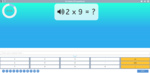
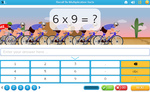
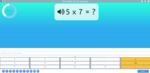
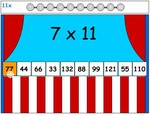
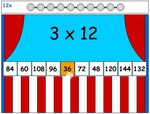
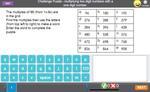
Samples: Learning 6x tables. Learning 7x tables. Learning 9x tables. 11x tables. 12x tables. Dividing by 6. Dividing by 7.
-
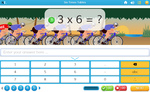
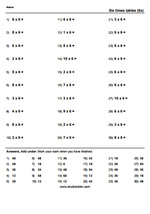
6x tables
- Activities: 7 course, 4 extra
-
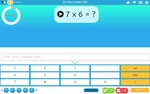
7x tables
- Activities: 7 course, 5 extra
-
9x tables
- Activities: 7 course, 6 extra
-
11x tables
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
12x tables
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
Dividing by 6
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
Dividing by 7
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
Dividing by 9
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.MD.2 – Use place value, known and derived facts to multiply and divide mentally, including: multiplying by 0 and 1; dividing by 1; multiplying together 3 numbers
-
14 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Tricky 20. Division facts. Multiplying by 10, 100 and 1000. Multiplying by 100. Learning 6x tables. Learning 7x tables.
-
2x-10x tables
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
Division facts
- Activities: 5 course, 9 extra
-
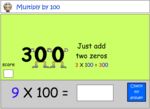
Multiplying by 10
- Activities: 4 course, 7 extra
-
Multiplying by 100
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
6x times tables (Skill 50)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
7x times tables (Skill 51)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
9x times tables (Skill 53)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
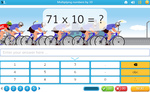
Multiplying by 10 (Skill 57)
- Activities: 6 course, 7 extra
-
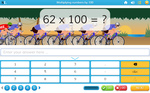
Multiplying by 100 (Skill 58)
- Activities: 5 course, 1 extra
-
Multiplying lots of 10 by a single digit number (Skill 66)
- Activities: 6 course, 7 extra
-
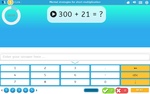
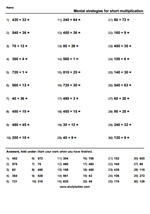
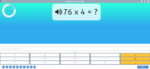
Mental strategies for short multiplication (Skill 68)
- Activities: 4 course, 1 extra
-
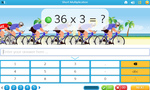
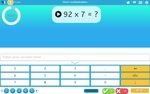
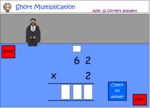
Short multiplication (Skill 69)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
Dividing multiples of 10 by a single digit number (Skill 70)
- Activities: 5 course, 1 extra
-
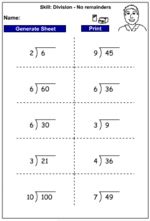
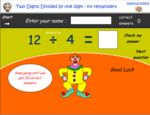
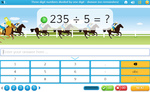
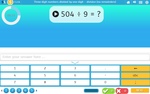
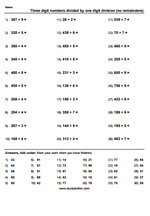
Dividing 3 digits by 1 digit - no remainders (Skill 71)
- Activities: 5 course, 7 extra
-
-
14 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.MD.3 – Recognise and use factor pairs and commutativity in mental calculations
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Factors. Identifying multiples. Factor trees. Identifying factors. Identifying factors: Activity 1.
-
Identifying factors
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
Identifying multiples
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Factor trees
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
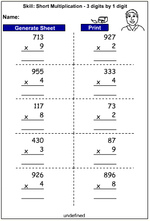
KS2.Y4.N.MD.4 – Multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one-digit number using formal written layout
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Multiplying 2 by 1 digit (mental strategy). Multiplying two-digits by one-digit. Multiplying 2 by 1 digit.
-
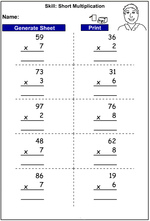
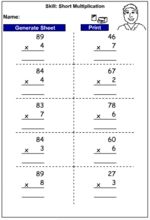
Multiplying a two-digit number by a one-digit number
- Activities: 1 course, 2 extra
-
Multiplying a two-digit number by a one-digit number - written strategy
- Activities: 4 course, 10 extra
-
Multiplying a two-digit number by a one-digit number - mental strategy
- Activities: 3 course, 10 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.MD.5 – Solve problems involving multiplying and adding, including using the distributive law to multiply two-digit numbers by 1 digit, integer scaling problems and harder correspondence problems such as n objects are connected to m objects
-
13 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: 6x tables (problem solving). 7x tables (problem solving). 9x tables (problem solving).
-
6x tables (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 6 extra
-
7x tables (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 6 extra
-
9x tables (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
2x-10x tables (problem solving)
- Activities: 4 course, 9 extra
-
2x-10x tables - puzzle
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying by 10 or 100 (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiples of 10 by 1 digit - problem solving
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Multiplying multiples of 10 - puzzle
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying 2 digits by a 1 digit number - Puzzle
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying 2 by 1 digit (missing number)
- Activities: 2 course, 7 extra
-
Dividing by 6 (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 4 extra
-
Dividing by 7 (problem solving)
- Activities: 4 course, 3 extra
-
Division facts (problem solving)
- Activities: 1 course, 6 extra
-
-
13 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F – Number - fractions (including decimals)
Pupils should be taught to:
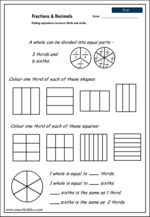
KS2.Y4.N.F.1 – Recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common equivalent fractions
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Modelling equivalent fractions. Matching equivalent fractions. Equivalence.
-
Modelling equivalent fractions
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.2 – Count up and down in hundredths; recognise that hundredths arise when dividing an object by 100 and dividing tenths by 10
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Hundredths - simplest form. Common decimals from 0 to 1 (tenths). Converting 10ths and 100ths to decimals.
-
Tenths and hundredths
- Activities: 4 course, 4 extra
-
Common decimals from 0 to 1 (tenths)
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Converting 10ths and 100ths to decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.3 – Solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, including non-unit fractions where the answer is a whole number
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Fractions.
-
Multiplying fractions by a whole number - visual
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.4 – Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding fraction with common denominators tutorial. Adding fractions with common denominators.
-
Add and subtract fractions (same denominators)
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.5 – Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Comparing fractions and decimals.
-
Comparing fractions and decimals (10ths 100ths)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.6 – Recognise and write decimal equivalents to ¼ ,½ , ¾
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Matching fractions to decimals. Fractions Problem Solving. Fractions Problem Solving.
-
Matching fractions to decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 2 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.7 – Find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as ones, tenths and hundredths
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Dividing a whole number by 10. Dividing whole numbers by 10 (problem solving). Dividing a whole number by 100.
-
Dividing whole numbers by 10 (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.N.F.8 – Round decimals with 1 decimal place to the nearest whole number
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Rounding decimals to whole numbers.
-
Rounding decimals to whole numbers
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
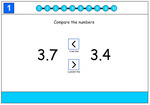
KS2.Y4.N.F.9 – Compare numbers with the same number of decimal places up to 2 decimal places
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
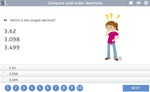
Samples: Placing Decimals On A Number Line. Compare and order decimals. Decimals on the number line. Compare Decimal Numbers.
-
Decimals on a number line.
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
Compare and order decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
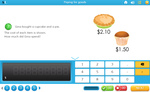
KS2.Y4.N.F.10 – Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to 2 decimal places
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Multiplying Decimals By A Single Digit Number. Fractions Problem Solving. Multiplying decimals by a whole number.
-
Multiplying decimals by a whole number
- Activities: 2 course, 6 extra
-
Simple fractions of quantities (problem solving)
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.M – Measurement
Pupils should be taught to:
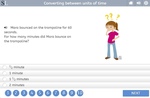
KS2.Y4.M.1 – Convert between different units of measure [for example, kilometre to metre; hour to minute]
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Converting between grams and kilograms. Converting between units of time. Converting between units of time II.
-
Converting between grams and kilograms
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Convert between units of time
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
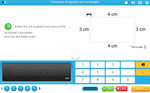
KS2.Y4.M.2 – Measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres and metres
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Perimeter. Perimeter of squares and rectangles. Calculating Perimeter Regular Shapes.
-
Perimeter of squares and rectangles.
- Activities: 3 course, 4 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
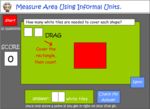
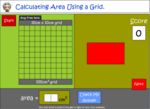
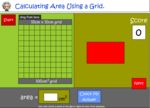
KS2.Y4.M.3 – Find the area of rectilinear shapes by counting squares
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Area using square tiles. Measure using square centimetres. Measure using square centimetres.
-
Area using square tiles
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Area using a grid.
- Activities: 4 course, 10 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
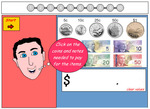
KS2.Y4.M.4 – Estimate, compare and calculate different measures, including money in pounds and pence
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Budgeting and Expenses. Paying with currencies from around the world. Different payment options. Units of measure.
-
Budgeting
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
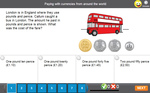
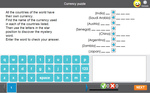
Currencies around the world
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
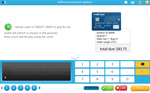
Payment options
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Units when measuring length (mm)
- Activities: 4 course, 3 extra
-
Measure volume using centicubes
- Activities: 6 course, 6 extra
-
Choosing appropriate units for measuring volume (mL or L)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
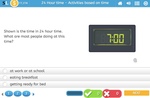
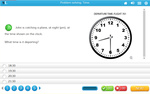
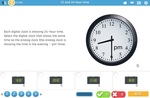
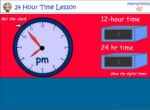
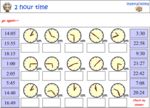
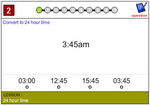
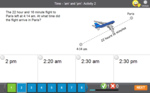
KS2.Y4.M.5 – Read, write and convert time between analogue and digital 12- and 24-hour clocks
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: 24 hour time. 24 hour time - am or pm. 24 Hour Time: Convert to 'am' or 'pm'.
-
24-hour time
- Activities: 8 course, 7 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
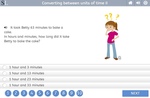
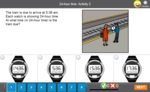
KS2.Y4.M.6 – Solve problems involving converting from hours to minutes, minutes to seconds, years to months, weeks to days
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Time - 'am' and 'pm': Activity 2. Challenge puzzle -perimeter. Two step problem solving. Two step problem solving.
-
Use a.m. and p.m.
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Challenge puzzle -perimeter
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Two step problem solving
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Two step problem solving
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.G.PS – Geometry - properties of shapes
Pupils should be taught to:
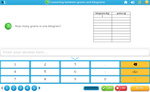
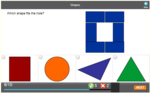
KS1.Y4.G.PS.1 – Compare and classify geometric shapes, including quadrilaterals and triangles, based on their properties and sizes
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Shapes. Splitting shapes. Properties of two-dimensional shapes. Grouping shapes based on attributes.
-
Describe two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
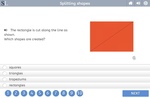
Splitting shapes
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Attributes of two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Grouping shapes based on attributes
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
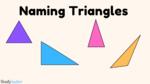
Naming triangles
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Prisms and pyramids
- Activities: 2 course, 8 extra
-
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
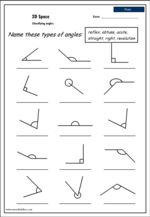
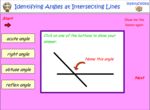
KS1.Y4.G.PS.2 – Identify acute and obtuse angles and compare and order angles up to 2 right angles by size
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Measuring obtuse angles using a protractor. Estimating the size of angles. Types of angles.
-
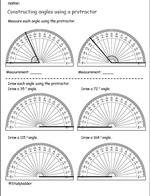
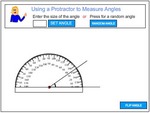
Measuring obtuse angles using a protractor
- Activities: 1 course, 3 extra
-
Estimate the size of angles.
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
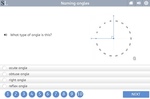
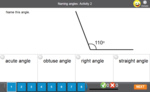
Naming angles
- Activities: 5 course, 3 extra
-
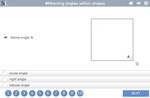
Naming angles within shapes
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
KS1.Y4.G.PS.3 – Identify lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes presented in different orientations
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Symmetry in the environment. Identify line of symmetry. Line of symmetry.
-
Symmetry - man-made structures
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Lines of symmetry
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
KS1.Y4.G.PS.4 – Complete a simple symmetric figure with respect to a specific line of symmetry
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Creating Symmetrical Drawings and Patterns. Symmetrical patterns and pictures. Creating symmetrical patterns.
-
Drawing symmetrical pictures
- Activities: 0 course, 4 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.G.PD – Geometry - position and direction
Pupils should be taught to:
KS2.Y4.G.PD.1 – Describe positions on a 2-D grid as coordinates in the first quadrant
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
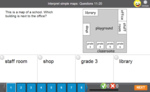
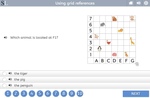
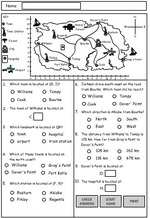
Samples: Interpret simple maps - the zoo. Using grid references. Simple maps. Maps (coordinates).
-
Interpret simple maps
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
Using grid references
- Activities: 2 course, 10 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.G.PD.2 – Describe movements between positions as translations of a given unit to the left/right and up/down
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Identify transformations - pictures. Identify transformations - shapes.
-
Transformations
- Activities: 2 course, 2 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
KS2.Y4.G.PD.3 – Plot specified points and draw sides to complete a given polygon
KS2.Y4.S – Statistics
Pupils should be taught to:
KS2.Y4.S.1 – Interpret and present discrete and continuous data using appropriate graphical methods, including bar charts and time graphs
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
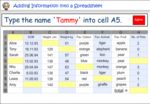
Samples: Interpreting Dot Plots. Adding information to a spreadsheet. Display data using dot plots.
-
Dot plots
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
Interpret data presented in a spreadsheet
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
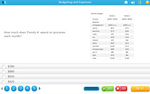
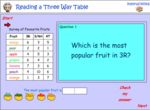
KS2.Y4.S.2 – Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in bar charts, pictograms, tables and other graphs
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
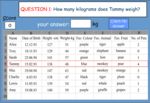
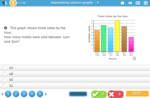
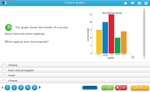
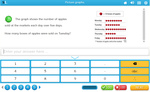
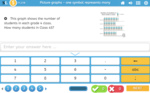
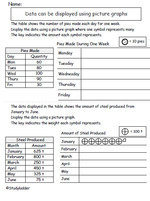
Samples: Interpreting column graphs - 5. Picture graphs - one symbol represents many. Reading a three way table.
-
Column graphs
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Picture graphs where one symbol represents many
- Activities: 3 course, 1 extra
-
Interpret data presented in two way tables.
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view