Mathematics – United States – Common Core State Standards
5.OA – Operations & Algebraic Thinking
Mathematics
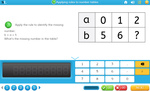
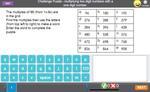
5.OA.1 – Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
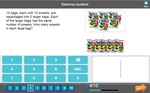
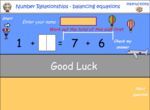
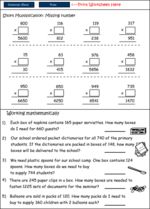
Samples: Brackets in number operations. Brackets in number operations - Two Step. Balancing equations.
-
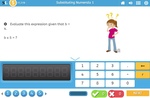
Brackets in number operations
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Brackets in number operations - Two Step
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
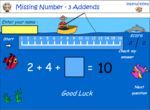
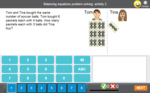
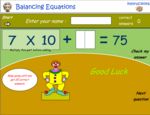
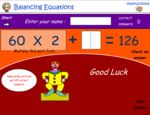
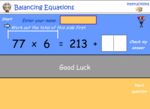
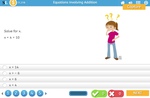
Balancing equations - Equivalent number sentences
- Activities: 4 course, 2 extra
-
Balancing equations - Equivalent number sentences
- Activities: 5 course, 10 extra
-
Challenge puzzle - balancing equations
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Order of operations : Multiply before adding
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
Order of operations - Multiply before subtracting
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Order of operations - mixed
- Activities: 4 course, 2 extra
-
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
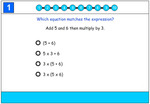
5.OA.2 – Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Continue number patterns. Rules defining number patterns. Applying rules to number tables. Order of Operations.
-
Continuing number patterns
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Rules defining number patterns
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Applying rules to number tables
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Order of Operations
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Numbers
- Activities: 1 course, 5 extra
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
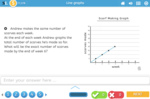
5.OA.3 – Generate two numerical patterns using two given rules. Identify apparent relationships between corresponding terms. Form ordered pairs consisting of corresponding terms from the two patterns, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 0, and given the rule “Add 6” and the starting number 0, generate terms in the resulting sequences, and observe that the terms in one sequence are twice the corresponding terms in the other sequence. Explain informally why this is so.
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Identifying expressions. Continuing number sequences including fractions and decimals.
-
Identifying expressions
- Activities: 1 course, 2 extra
-
Continuing number sequences
- Activities: 1 course, 4 extra
-
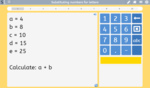
Substituting numbers for letters
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Substituting Numerals
- Activities: 1 course, 4 extra
-
Subtraction of Like Terms
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Patterns and Algebra
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
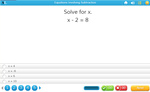
Equations Involving Subtraction
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NBT – Number & Operations in Base Ten
Mathematics
5.NBT.1 – Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left.
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Multiplying by 10, 100 and 1000. Multiplying by 100. Multiplying by 10 or 100. Multiplying decimals by 1000.
-
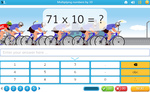
Multiplying by 10
- Activities: 4 course, 7 extra
-
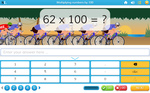
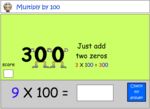
Multiplying by 100
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiplying by 10 or 100 (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiplying decimals by 1000
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Dividing whole numbers by 100
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying decimals by a whole number
- Activities: 2 course, 6 extra
-
Multiplying decimals by 10
- Activities: 2 course, 4 extra
-
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NBT.2 – Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10, and explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when a decimal is multiplied or divided by a power of 10. Use whole-number exponents to denote powers of 10.
-
12 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Multiplying by 10, 100 and 1000. Multiplying by 100. Multiplying by 10 or 100.
-
Multiplying by 10
- Activities: 4 course, 7 extra
-
Multiplying by 100
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiplying by 10 or 100 (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiplying multiples of 10 (problem solving)
- Activities: 2 course, 1 extra
-
Multiplying multiples of 10 - puzzle
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying multiples of 10 (missing number)
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiplying by multiples of ten
- Activities: 4 course, 12 extra
-
Dividing multiples of 10 by 1 digit
- Activities: 4 course, 2 extra
-
Dividing multiples of 10 by 1 digit (problem solving)
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Revision
- Activities: 5 course, 4 extra
-
Dividing whole numbers by 100
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Long division
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
-
12 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NBT.3 – Read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths.
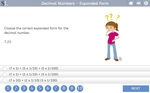
5.NBT.3.a – Read and write decimals to thousandths using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form, e.g., 347.392 = 3 × 100 + 4 × 10 + 7 × 1 + 3 × (1/10) + 9 × (1/100) + 2 × (1/1000).
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Decimal Numbers - Expanded Form. Common decimals from 0 to 1 (tenths). Compare and order decimals.
-
Decimal Numbers - Expanded Form
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Common decimals from 0 to 1 (tenths)
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
Compare and order decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
Read and write decimals in the thousandths
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Comparing decimals in the thousandths
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Place value (thousandths)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Place value - thousandths
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NBT.3.b – Compare two decimals to thousandths based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Compare and order decimals. Read and write decimals in the thousandths. Comparing decimals in the thousandths.
-
Compare and order decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
Read and write decimals in the thousandths
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Comparing decimals in the thousandths
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Place value (thousandths)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Place value - thousandths
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NBT.4 – Use place value understanding to round decimals to any place.
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Rounding decimals to whole numbers.
-
Rounding decimals to whole numbers
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
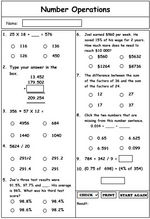
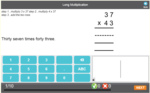
5.NBT.5 – Fluently multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Multiplying 2 by 1 digit (mental strategy). Multiplying two-digits by one-digit. Multiplying 2 by 1 digit.
-
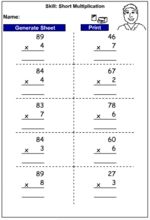
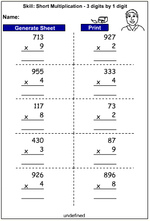
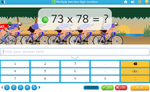
Multiplying a two-digit number by a one-digit number
- Activities: 1 course, 2 extra
-
Multiplying a two-digit number by a one-digit number - written strategy
- Activities: 4 course, 10 extra
-
Multiplying a two-digit number by a one-digit number - mental strategy
- Activities: 3 course, 10 extra
-
Multiplying 2 digits by a 1 digit number - Puzzle
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
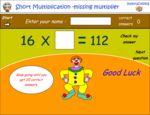
Multiplying 2 by 1 digit (missing number)
- Activities: 2 course, 7 extra
-
Multiplying by 2 digit numbers (problem solving)
- Activities: 1 course, 4 extra
-
Multiplying two-digit numbers
- Activities: 5 course, 10 extra
-
-
7 learning outcomes – click to view
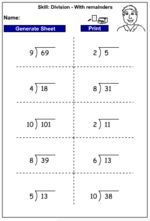
5.NBT.6 – Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to four-digit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
-
11 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Challenge Puzzle - Division of a large number by a one digit number.
-
Division puzzle
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying multiples of 10 (missing number)
- Activities: 3 course, 8 extra
-
Multiplying 2 by 1 digit (missing number)
- Activities: 2 course, 7 extra
-
Dividing multiples of 10 by 1 digit
- Activities: 4 course, 2 extra
-
Dividing multiples of 10 by 1 digit (problem solving)
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Dividing 3 digits by 1 digit (problem solving)
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
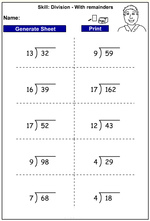
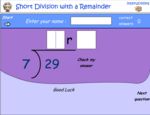
Division (with remainders)
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
Dividing 4-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers
- Activities: 4 course, 5 extra
-
Dividing large numbers (problem solving)
- Activities: 1 course, 3 extra
-
Long division
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
Long division - problem solving
- Activities: 0 course, 4 extra
-
-
11 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NBT.7 – Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding Decimals. Subtracting Decimals. Multiplying Decimals By A Single Digit Number. Dividing a whole number by 10.
-
Adding decimals
- Activities: 5 course, 3 extra
-
Subtracting decimals
- Activities: 4 course, 3 extra
-
Multiplying decimals by a whole number
- Activities: 2 course, 6 extra
-
Dividing whole numbers by 10 (problem solving)
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
Matching fractions, decimals and percentages.
- Activities: 3 course, 6 extra
-
Percentages as Decimals
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying decimals by decimals
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Changing mixed fractions to decimals
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
-
8 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF – Number & Operations—Fractions
Mathematics
5.NF.1 – Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given fractions with equivalent fractions in such a way as to produce an equivalent sum or difference of fractions with like denominators. For example, 2/3 + 5/4 = 8/12 + 15/12 = 23/12. (In general, a/b + c/d = (ad + bc)/bd.)
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Adding and subtracting related fractions. Adding mixed fractions. Adding and subtracting fractions.
-
Adding and subtracting related fractions
- Activities: 6 course, 1 extra
-
Adding mixed fractions
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Adding and subtracting fractions
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF.2 – Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole, including cases of unlike denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. Use benchmark fractions and number sense of fractions to estimate mentally and assess the reasonableness of answers. For example, recognize an incorrect result 2/5 + 1/2 = 3/7, by observing that 3/7 < 1/2.
Mathematics
5.NF.3 – Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (a/b = a ÷ b). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem. For example, interpret 3/4 as the result of dividing 3 by 4, noting that 3/4 multiplied by 4 equals 3, and that when 3 wholes are shared equally among 4 people each person has a share of size 3/4. If 9 people want to share a 50-pound sack of rice equally by weight, how many pounds of rice should each person get? Between what two whole numbers does your answer lie?
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Converting Improper Fractions. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions tutorial.
-
Improper and mixed number fractions
- Activities: 6 course, 1 extra
-
Converting mixed numbers to improper frac.
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Division- answers as fractions
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF.4 – Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication to multiply a fraction or whole number by a fraction.
5.NF.4.a – Interpret the product (a/b) × q as a parts of a partition of q into b equal parts; equivalently, as the result of a sequence of operations a × q ÷ b. For example, use a visual fraction model to show (2/3) × 4 = 8/3, and create a story context for this equation. Do the same with (2/3) × (4/5) = 8/15. (In general, (a/b) × (c/d) = ac/bd.)
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Dividing whole numbers by fractions. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions.
-
Dividing whole numbers by fractions
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
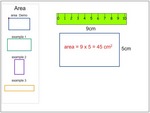
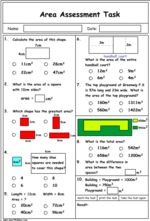
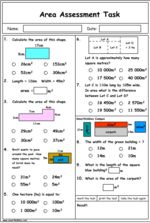
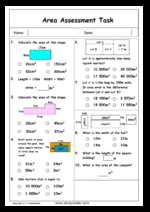
5.NF.4.b – Find the area of a rectangle with fractional side lengths by tiling it with unit squares of the appropriate unit fraction side lengths, and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths. Multiply fractional side lengths to find areas of rectangles, and represent fraction products as rectangular areas.
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Calculating area. Area (problem solving). Area of Squares and Rectangles. Area of Squares and Rectangles.
-
Calculating area (squares and rectangles)
- Activities: 5 course, 9 extra
-
Area (problem solving)
- Activities: 1 course, 6 extra
-
Area of Squares and Rectangles
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF.5 – Interpret multiplication as scaling (resizing), by:
5.NF.5.a – Comparing the size of a product to the size of one factor on the basis of the size of the other factor, without performing the indicated multiplication.
5.NF.5.b – Explaining why multiplying a given number by a fraction greater than 1 results in a product greater than the given number (recognizing multiplication by whole numbers greater than 1 as a familiar case); explaining why multiplying a given number by a fraction less than 1 results in a product smaller than the given number; and relating the principle of fraction equivalence a/b = (n × a)/(n × b) to the effect of multiplying a/b by 1.
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Fractions. Fractions Problem Solving. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions. Fractions Problem Solving.
-
Multiplying fractions by a whole number - visual
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying fractions
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
-
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
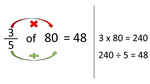
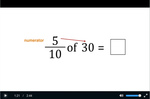
5.NF.6 – Solve real world problems involving multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers, e.g., by using visual fraction models or equations to represent the problem.
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Fractions Problem Solving.
-
Simple fractions of quantities (problem solving)
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF.7 – Apply and extend previous understandings of division to divide unit fractions by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions. (Students able to multiply fractions in general can develop strategies to divide fractions in general, by reasoning about the relationship between multiplication and division. But division of a fraction by a fraction is not a requirement at this grade.)
5.NF.7.a – Interpret division of a unit fraction by a non-zero whole number, and compute such quotients. For example, create a story context for (1/3) ÷ 4, and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient. Use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (1/3) ÷ 4 = 1/12 because (1/12) × 4 = 1/3.
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Fractions of a number. Fractions Problem Solving. Division - Answers as fractions. Fractions Problem Solving.
-
Fractions of a number
- Activities: 12 course, 2 extra
-
Simple fractions of quantities (problem solving)
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
Division- answers as fractions
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying fractions
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
-
Dividing whole numbers by fractions
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF.7.b – Interpret division of a whole number by a unit fraction, and compute such quotients. For example, create a story context for 4 ÷ (1/5), and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient. Use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that 4 ÷ (1/5) = 20 because 20 × (1/5) = 4.
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Fractions Problem Solving. Multiplying and Dividing Fractions. Fractions Problem Solving. Multiplying fractions.
-
Multiplying fractions
- Activities: 0 course, 3 extra
-
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
5.NF.7.c – Solve real world problems involving division of unit fractions by non-zero whole numbers and division of whole numbers by unit fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, how much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 1/3-cup servings are in 2 cups of raisins?
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Dividing whole numbers by fractions. Divide whole numbers by fractions (problem solving).
-
Dividing whole numbers by fractions
- Activities: 3 course, 0 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
5.MD – Measurement & Data
Mathematics
5.MD.1 – Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world problems.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Units of measure. Converting between units of volume: Activity 2. Converting between grams and kilograms. Length.
-
Converting between kilometers and meters
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Problem solving : Volume
- Activities: 0 course, 5 extra
-
Converting between grams and kilograms
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Length - problem solving
- Activities: 4 course, 1 extra
-
Length - problem solving
- Activities: 3 course, 4 extra
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
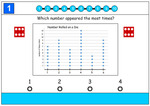
5.MD.2 – Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Use operations on fractions for this grade to solve problems involving information presented in line plots. For example, given different measurements of liquid in identical beakers, find the amount of liquid each beaker would contain if the total amount in all the beakers were redistributed equally.
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Interpreting Dot Plots. Interpret a dot plot. Line graphs. Display data using dot plots. Line Plots. Line graphs.
-
Dot plots
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
Dot plots
- Activities: 1 course, 2 extra
-
Line graphs
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
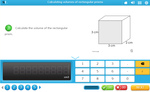
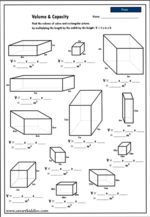
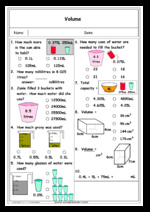
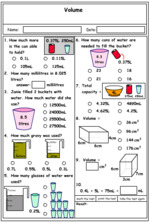
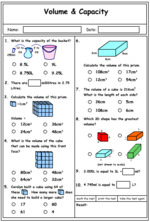
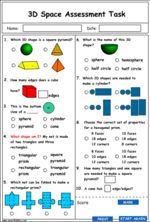
5.MD.3 – Recognize volume as an attribute of solid figures and understand concepts of volume measurement.
5.MD.3.a – A cube with side length 1 unit, called a “unit cube,” is said to have “one cubic unit” of volume, and can be used to measure volume.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
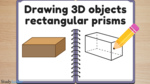
Samples: Calculating volume. Volume Extension. Drawing 3D objects. Matching - three-dimensional objects with their nets.
-
Volume of rectangular prisms
- Activities: 4 course, 6 extra
-
Volume
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
Drawing three-dimensional objects
- Activities: 11 course, 9 extra
-
Nets of three dimensional objects
- Activities: 4 course, 4 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
5.MD.3.b – A solid figure which can be packed without gaps or overlaps using n unit cubes is said to have a volume of n cubic units.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Calculate the volume of a stack - record in cubic centimetres. Volume and Capacity. Calculating volume.
-
Measure volume using centicubes
- Activities: 6 course, 6 extra
-
Volume and Capacity
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
Volume of rectangular prisms
- Activities: 4 course, 6 extra
-
Volume
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
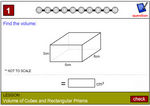
5.MD.4 – Measure volumes by counting unit cubes, using cubic cm, cubic in, cubic ft, and improvised units.
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Calculate the volume of a stack - record in cubic centimetres.
-
Measure volume using centicubes
- Activities: 6 course, 6 extra
-
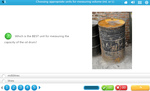
Choosing appropriate units for measuring volume (mL or L)
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Volume and Capacity
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
Volume of rectangular prisms
- Activities: 4 course, 6 extra
-
Volume
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
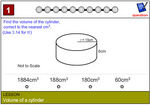
Volume of a Cylinder
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
-
6 learning outcomes – click to view
5.MD.5 – Relate volume to the operations of multiplication and addition and solve real world and mathematical problems involving volume.
5.MD.5.b – Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with whole-number side lengths by packing it with unit cubes, and show that the volume is the same as would be found by multiplying the edge lengths, equivalently by multiplying the height by the area of the base. Represent threefold whole-number products as volumes, e.g., to represent the associative property of multiplication.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Calculating volume. Calculate the volume of a stack - record in cubic centimetres. Volume and Capacity.
-
Volume of rectangular prisms
- Activities: 4 course, 6 extra
-
Measure volume using centicubes
- Activities: 6 course, 6 extra
-
Volume and Capacity
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
Volume
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
Volume of a Cylinder
- Activities: 0 course, 1 extra
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
5.MD.5.c – Apply the formulas V = l × w × h and V = b × h for rectangular prisms to find volumes of right rectangular prisms with whole-number edge lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
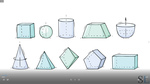
Samples: Calculating volume. Matching - three-dimensional objects with their nets. Naming prisms and pyramids.
-
Volume of rectangular prisms
- Activities: 4 course, 6 extra
-
Nets of three dimensional objects
- Activities: 4 course, 4 extra
-
Prisms and pyramids
- Activities: 2 course, 8 extra
-
Challenge Puzzle - prisms and pyramids
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Volume and Capacity
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
5.MD.5.d – Recognize volume as additive. Find volumes of solid figures composed of two non-overlapping right rectangular prisms by adding the volumes of the non-overlapping parts, applying this technique to solve real world problems.
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Calculating volume. Volume and Capacity. Volume Extension. Calculating volumes of rectangular prisms.
-
Volume of rectangular prisms
- Activities: 4 course, 6 extra
-
Volume and Capacity
- Activities: 3 course, 7 extra
-
Volume
- Activities: 0 course, 2 extra
-
-
3 learning outcomes – click to view
5.MD – Measurement & Data
Mathematics
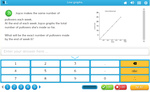
5.G.1 – Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and the coordinates correspond (e.g., x-axis and x-coordinate, y-axis and y-coordinate).
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
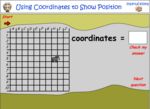
Samples: Cartesian Plane - Identify location. Cartesian Plane - Identify coordinates. Cartesian planes - lines and shapes.
-
Cartesian Planes
- Activities: 3 course, 5 extra
-
-
1 learning outcomes – click to view
5.G.2 – Represent real world and mathematical problems by graphing points in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane, and interpret coordinate values of points in the context of the situation.
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
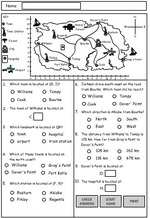
Samples: Using grid references. Using Coordinates to Read a Map. Maps (coordinates). Describe locations using grid reference.
-
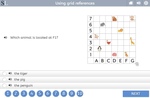
Using grid references
- Activities: 2 course, 10 extra
-
Location using a grid reference.
- Activities: 1 course, 1 extra
-
-
2 learning outcomes – click to view
Mathematics
5.G.3 – Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that category. For example, all rectangles have four right angles and squares are rectangles, so all squares have four right angles.
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
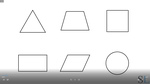
Samples: Properties of two-dimensional shapes. Grouping shapes based on attributes. Constructing 2D shapes.
-
Attributes of two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Grouping shapes based on attributes
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Construct and draw two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
Naming triangles
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
4 learning outcomes – click to view
5.G.4 – Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view
Samples: Splitting shapes. Constructing 2D shapes. Properties of two-dimensional shapes. Grouping shapes based on attributes.
-
Splitting shapes
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Construct and draw two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 3 course, 3 extra
-
Attributes of two dimensional shapes
- Activities: 2 course, 0 extra
-
Grouping shapes based on attributes
- Activities: 1 course, 0 extra
-
Naming triangles
- Activities: 4 course, 0 extra
-
-
5 learning outcomes – click to view